Machine vision has emerged as a disruptive technology in virtually every sector — yet many business leaders still aren’t clear on what it truly is or how it operates. At its most basic level, machine vision offers a digital version of human visual perception, yet its potential goes well beyond simple image recognition.
Below, we’ll break down the specifics of how this technology works, the benefits of machine vision in the supply chain and logistics sector, and how to best integrate it into your own business operations.
What is Machine Vision Technology?
Machine Vision (MV) Technology encompasses all of the devices and systems required to both capture and interpret images digitally. By integrating computer vision, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, MV effectively mimics human perception — enabling automated systems to recognize components, products, and patterns, then act on that information in real time. These systems consist of digital sensors within industrial cameras and rely on specialized software for accurate image processing and analysis, enabling tasks like visual inspection, defect detection, and robot guidance in industrial automation.
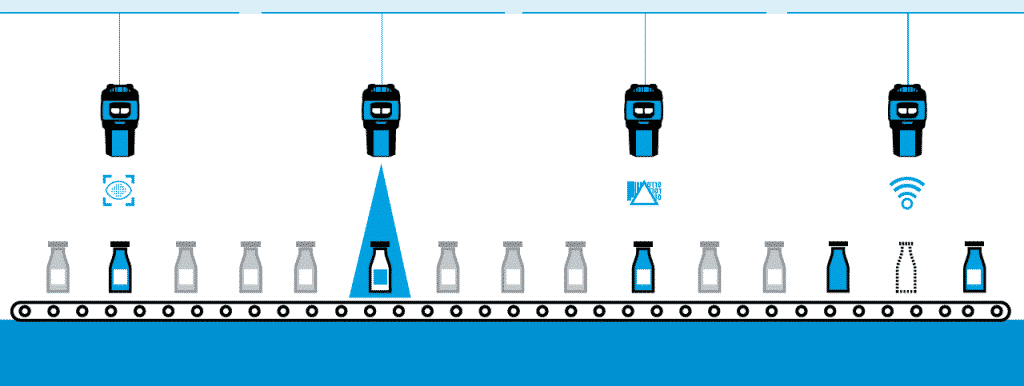
The core components of a machine vision system typically include high-resolution cameras, lenses, lighting, image-processing hardware, and sophisticated software. Working together in real time, these elements capture and analyze visual data to maintain consistent product quality, improve operational accuracy, and support a wide range of complex tasks in manufacturing and logistics.
How Does Machine Vision Work?
Now that you have a basic idea of what machine vision technology is, let’s break down the steps that allow these automated systems to replicate — and often outperform — the human eye.
Digital Sensors Capture Light
Machine vision systems rely on high-speed image sensors to detect when packages, pallets, or other objects are present. These sensors can capture light via complementary metal–oxide–semiconductors (CMOS) or charge-coupled devices (CCD). Both CMOS and CCD make it possible to convert captured light to pixels, which represent light intensity in specific areas.
Vision sensors with higher resolutions produce images containing more pixels, enhancing image quality and making it easier to discern visual details. High-resolution images are crucial for accurate pattern recognition and defect detection.
Frame grabbers play a key role in capturing high-resolution images in a variety of settings. These components obtain still frames in digital form, often performing real-time compression or otherwise preparing images for analysis. Frame grabbers can be used alongside or in place of smart cameras, ensuring that high-speed, detailed images are ready for further processing and analysis.
Image Processing and Image Analysis
Image processing and analysis follow sensor detection in the MV system, playing a critical role in the production line. This stage leverages data from the digital images captured by the sensors. Pre-processing techniques, such as filtering and noise reduction, may be applied to optimize images for accurate measurements, enhancing quality assurance in the manufacturing process.
The processed image undergoes vision inspection to identify and isolate features that need to be measured or observed. Vision processing determines which features are important for quality assurance. Once the necessary measurements are collected, they are compared against predefined criteria to ensure they meet the required standards. This rigorous analysis helps to detect defects, reduce downtime, and minimize human error, ultimately improving the efficiency and reliability of processes such as manufacturing.
Machine Vision Plus Barcode Scanning
In logistics, machine vision is often used alongside barcode systems — including fixed industrial scanners — to provide an alternative to traditional employee-based scanning. Machine vision systems may incorporate Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to interpret data from captured images, which allows these systems to make judgments based on data extracted from captured images.
Before MV solutions were implemented, barcode scanning typically relied on human labor. This prevented workers from focusing on higher-level tasks, and human-based barcode reading and verification were time-intensive and error-prone. The integration of machine vision — often in tandem with or as an upgrade to fixed industrial scanners— helps reduce errors and free up personnel.
Currently, optimized MV barcode scanning involves a series of strategically placed cameras that can capture multiple sides of each pallet. These systems prove especially valuable prior to loading, as smart cameras minimize the likelihood of incorrect carriers or incomplete shipments.

What is Machine Vision Used for Today?
From healthcare to the automotive sector and even hospitality, machine vision can drive improvements in nearly every industry imaginable. Currently, machine vision applications are most notable in supply chain and logistics operations.
We’ve already touched on the value of MV barcode scanning, but that’s only the beginning. Further industrial applications include:
- Pick and pack sorting. Vision-guided robotic sorting solutions can dramatically improve accuracy and efficiency for pick and pack operations. They’re particularly effective when integrated with industrial robots. Machine vision cameras can easily be implemented to ensure that all steps within automated workflows are completed properly. Also, as previously mentioned, these cameras are able to rapidly read barcodes situated on various sides of packages.
- Package tracking. Track and trace systems increasingly incorporate machine vision, which provides exceptional oversight as products navigate not only the warehouse environment, but also the entire supply chain. This functionality is especially important in food and beverage processing, where elite traceability makes it possible to determine the point of origin for all ingredients.
 Quality control. Machine vision promotes nearly flawless quality control by removing the risk of human mistakes that commonly lead to returned orders. Robotic systems featuring machine vision excel as compared to their human counterparts. After all, while humans achieve a high level of discernment, their powers of perception can sometimes dull as a specific image is seen repeatedly and imprinted on the brain. Machine vision systems, however, capture accurate images every time. As such, MV solutions are already relied upon for everything from beer bottling to manufacturing, where they are able to close that defect detection gap.
Quality control. Machine vision promotes nearly flawless quality control by removing the risk of human mistakes that commonly lead to returned orders. Robotic systems featuring machine vision excel as compared to their human counterparts. After all, while humans achieve a high level of discernment, their powers of perception can sometimes dull as a specific image is seen repeatedly and imprinted on the brain. Machine vision systems, however, capture accurate images every time. As such, MV solutions are already relied upon for everything from beer bottling to manufacturing, where they are able to close that defect detection gap.- Safety verification and regulatory compliance. Similar to quality control, MV inspection systems may determine whether products or processes abide by safety protocol. For example, in food and beverage operations, machine vision systems may determine whether tamper-proof safety seals are present — and whether they’re used correctly.
The Future of this Technology
Machine vision has come a long way in the last few years, but its evolution is just beginning. Recent trends have included a shift towards the cloud, where high volumes of data generated are more easily accessible.
Cloud solutions enable enterprises to make better use of data generated via these systems, thereby ensuring that patterns are spotted and that these observations produce the necessary improvements. Cloud-optimized MV solutions also promote more efficient decision-making, as the cloud provides immediate access to real-time data.
MV technology is often highlighted as a key component of the expected fourth industrial revolution, which is typically referred to as Industry 4.0. Additional developments worth paying attention to include the following:
Alternate Lighting Solutions
Machine vision may soon be functional in a broader range of environments, as it may no longer rely solely on visible light.
Already, near-infrared (NIR) cameras are an option when a reliable light source isn’t available. All infrared imaging detects photons at different wavelengths, but because NIR sits closer to the visible spectrum, these cameras can produce sharper images than far-infrared options. This capability is particularly valuable for low-light settings, where human vision and conventional cameras often struggle to capture clear details.
Autonomous Vehicles
Machine vision is playing a valuable role in promoting the use of autonomous vehicles within numerous contexts. For example, self-driving forklifts are becoming an integral part of the modern warehouse environment, providing much-needed support for packing and palletizing.
Artificial intelligence and advanced algorithms will further elevate these autonomous systems, allowing them to function according to self-collected data regarding warehouse layouts and typical traffic patterns.
Harness the Power of Machine Vision With Peak Technologies
As the technology that underscores computer vision becomes even more complex, it will be crucial for businesses to work with professionals who understand how evolving systems can be effectively implemented. Strategic integration is essential, particularly in any logistics operation that relies on automation.
Our team at Peak Technologies offers assistance for cutting-edge machine vision solutions and other automation technologies that promise to revolutionize the supply chain sector. Our field service engineers can help you determine which applications are most relevant to your enterprise — and how they can be implemented to deliver the highest possible ROI.
Customized end-to-end solutions should be tailored to the unique needs of every enterprise. At Peak Technologies, we guarantee personalized services that work effectively within your operations’ requirements. Contact us today to learn more about options for integrating machine vision systems into your operations.